#ibm mainframe access
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Mainframe access for learning!
Get the opportunity to level up your tech expertise in Mainframe!
🔹 Gain practical experience on real mainframe systems 🔹 Access to cutting-edge tools and resources 🔹 Elevate your career with in-demand mainframe skills
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
IBM Mainframe Access providers companies in USA
Find the right place for your mainframe requirement, check the list of companies that offer IBM mainframe access in USA
Rocket Software
Relational Architects International
Software Engineering of America
ASPG
Deloitte US
Maintec
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Back in an era when computers were the size of a room and only government agencies and large companies could afford to have one, IBM was king of the mainframes. But they had a lineup of several incompatible computers, some intended for scientific uses (the IBM 7090/7094), others were for commercial uses (the IBM 7080 and IBM 7010). IBM wanted to have a single unified architecture so that software could be exchanged between them and customers could upgrade from cheaper, lower powered machines to more higher powered ones.
What came out of it was the IBM System/360 line of mainframes (referring to the concept of "360 degrees" making up a circle) that ended up being the dominant mainframe computer for decades to come, it got cloned by competitors, and its descendants are still being produced to this day.
The IBM System/360 had many features that since then became foundational for modern computing.
An entirely binary number system. While some computers (such as the IBM 7090) used a binary system, others operated exclusively in decimal mode, encoded using binary coded decimals using 4 bits for each digit (such as the IBM 7080 and IBM 7010). Others went a step further and were only capable of storing decimal digits 0 to 9 (like the IBM 7070).
To store textual information, each character was stored in 8 bits, establishing the dominance of 8 bit bytes. Previous systems would typically use 6 bits to store text, and would usually only enable a single case of letters. The IBM 7070 didn't provide access to bits and characters were stored in 2 decimal digits. It was also one of the first machines to support the then new ASCII standard, although notably it provided much better support for IBM's proprietary EBCDIC encodings which came to dominate mainframe computing.
Even though it was a 32-bit system, memory was byte addressed. Previous systems would access memory one word at a time (for the IBM 7090, this was 36 bits per word, for the IBM 7010, this was 10 digits plus a sign), or had variable length words and accessed them through their last digits (IBM 7080 and IBM 7010). The IBM System/360 however accessed 32-bit words as 4 bytes by their lowest address byte.
Two's complement arithmetic. Previous machines (even the binary IBM 7090) would encode numbers as sign/magnitude pairs, so for example -3 would be encoded identically to 3 except for the sign bit. Two's complement encoding, now the standard in modern computers, makes it much easier to handle signed arithmetic, by storing -3 as a large power of 2 minus 3.
69 notes
·
View notes
Note
I tried drawing reeda because I love her. I have no idea what you had in mind for her design so I just re-read the chapter and went off of what your description was the best that I could. She gives me Painter vibes from pressure

I LOVE THISSSSSSSSSSSSS THANK YOU!!!!!! Ford absolutely has a mini monitor like this in each room so he can see its messages!
Honestly REEDA's main design in my head fits Ford's lab, so it's a very retro cassette-futuristic style like you've illustrated. Think: how did people imagine the future was going to look in 197-something. All Commodores and IBM and thick plastic etc.
Ford's lab in mtb is designed with that exact aesthetic in mind, so terminals and things like this were at the forefront of my mind:
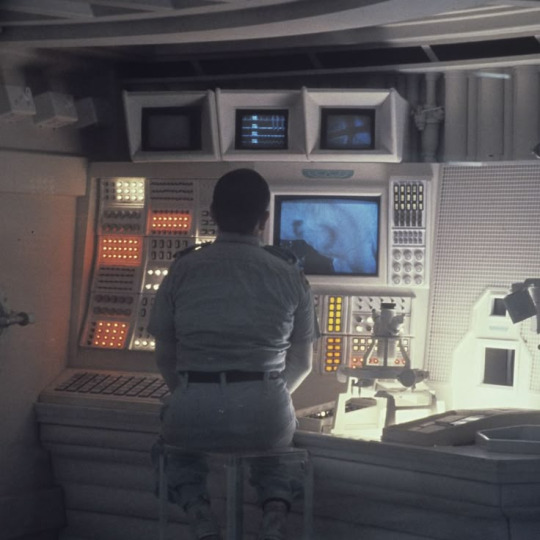



These types of terminals are primarily in the mainframe room that Reader goes through to access the lab. It's all set up with things like the above. Whereas REEDA's central screens in the main body of the lab look more like the ones in The Forbin Project:

Except they're a mix of both of those aesthetics, so they're weirdly long CRT monitors suspended in a similar layout to the above!

Here's another ss from Forbin bc it works along similar lines! And also it's a great movie and you should watch it!
#i really honestly think Ford's favourite movie is Alien#and so in mtb he just wanted a cool Nostromo type lab#and i thought the idea was funny and cute and in character so#also b u t t o n s#i think he's also incredibly nostalgic for a time he left behind and even though he dislikes tech when he leaves#he HAS to make use of it in alternate dimensions so grows a grudging acceptance for it#and i think he's AWFUL with earth tech and when he comes back and sees how minimalist everything is he hates it even more#but he's forced to engage with alien tech in his travels so he becomes used to it a bit more#and so he combines that aesthetic nostalgia with the advanced ability of alien tech#which is how he designs his lab#he prefers old-style ways of recording (his journals) but he knows he HAS to make use of digital record keeping to some extent#and he's come to understand its applications in foreign environments#so while he still records everything on paper#he utilises other aspects of tech if he has to#but he complains about it the whole time and he'd really just be happy with 8000 filing cabinets of a4 and a biro#but really considering all the information he retains and works on it means he needs a specialist set up#anyways shut UP fox we get it you like worldbuilding for this guy UGH enough#asks#ford asks#wb#mtb stuff#ALSO we do see that he makes use of tech in LL and so I think he makes himself get on with it where he has to#just to defend myself a bit#bc i know some people think he'd be very tech-phobic in general#but i disagree to a certain extent#like yes but actually also no#AND remember that Fidds installed REEDA#ford had no say in it#he just begrudgingly goes along with it and gradually learns that actually its quite useful (though he won't admit it)#anways I digress that was a real tirade for no real reason im just very passionate about Ford's experiences with alien tech
27 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi where you around in the seventies to actually expertise these Computers first hand
Yeah so I was a tween/teen in the 70s and was definitely around. I was fascinated with computers thanks to Star Trek and Lost in Space etc, but computers were very hard to come by then, no one owned one and they were limited access.
I did get time on our PDP-8 in high school, and sometime around 79 or so built my own system from a kit and was like the only kid on the block with a computer actually in his house.
Only other time I remember using a computer (mainframe, not counting video arcade games here) was at the university of Connecticut, thanks to a neighbor who was a professor there.
He took me in to show me their IBM mainframe and told me the computer could answer any yes or no question. So I asked it is it Wednesday, our neighbor typed it on the terminal, and it immediately printed "yes" in glowing green phosphor. I was freaked out, asked if it was Tuesday, and it said "no". I asked all sorts of questions, about how many people were in the room, math, geography etc.
Yes, no, yes.. it kept getting them all right!
After becoming convinced the computer was sentient, our neighbor showed me the program he had wrote. It let you type in text, and if you started the sentence with a space, it answered "yes", if not, "no". Observers did not notice the space. Genius.
Wrote this same program many times over the years to amaze people. Less amazing now with AI on our doorstep, so sorry y'all can't go impress your friends with this one anymore.
86 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pseudo-historical project about 1912 unit record equipment computation aka the "Symbolic Analyst Processor" full stack!



(above pictures emulate the looks of what this tech stack documentation and actual use may look like, still very early in the process though)
It is still coming together by my head as I write infodump notes and research various aspects of the whole time, (including the WIMP & MERN/MEAN stack) but yk, things are coming together nicely to give some milestone project mid-way between my current phase in life and the next where I go develop a fully alternative INTJ lively stack of tools. Explanations, history dives, lively reaction studies and a couple more content suggestions related to it are on the way.
Behold, the infodumps
"Top-bottom and back up workflow" 1910 / 1912 Unit Record Equipment Tabulator Computation "Bundle" Project (Pflaumen & Utalics' SymbolicAnalystProcessor)
Information Processing Language / LISP 1.5 / Bel, A-BASIC / DIBOL, Spreadsheets, Cellular Automaton, COS-310, magnetic tape storage too, TECO / VIM, Assembly, Wirebox, Tabulator, Alphanumeric Interpreter, Printer, RTTY device, Data Recording, Bulk Data Processing Indexed Cards, 60-64 entries Deque, 4K Direct-use RAM, 12K * 24 storage devices, Phonebook, Timeclock, DateTime Calendar, Programmable, Statistics, Demographics, Voting, Ledger, Journal, Logging, Rolodex, 12 Generic-use Registers & 4 Special Registers, Catalog, ~16 Keys Pad, Customized Hexadecimal Numeric Representation for "MachineCode" Hexdumps, 4*12 bits per page of data, Macros, Paracosm, may be useful for Military & Civilian Uses, Electrical Energy (and possibly incorporates some mechanical energy too), Nouns & Verbs, "Vector" XY plotter, Lambda Calculus / Panini Grammar / Universal Turing Machine Thesis, Rotors, Ural TriodeVaccumTube "Mainframe", Interactive-Use, Hypertext Interactive Video Terminal, Memex, Modem, Electric + Radio Telegraphy, Document-processing, Word-processing, Orange Plasma Touchscreen Terminal, Time-sharing, Cash Register, Bank, Automatic Teller Machine, Vending Machine, Oracle, Typewriter / Selectric, IBM 701, IBM 1440, IBM 403, IBM System/360, OpenPOWER, F#, IBM Tellum, MUD, TextWorld, solo text-adventures, Email, AIX, z/OS, Linux for IBM mainframes, Symbolic Processing System, Autocoder, modular, IBM Lotus Suite, interface with KDE or CDE, paper handling equipment, Addventure, 12-bit basic data unit as designated word, Distributed Interactive System, VeneraFS (cladogram Parade+DolDoc), GNU Hurd / MINIX3-style Microkernel, either permissive FLOSS license or public domain waiver, extensive documentation, printed illustrated booklets, music-playback, emulator / compiler / bytecode / interpreter, analog media-friendly, mostly for didactic tinkering educational uses, multilingual reconfigurable programming, HTML+CSS, Markdown, Argdown, DMA, hardware-friendly, software development environment for direct-access programmers and aesthetic designers, sub-version control system like Git, various hardware & software implementations, museum / observatory Toymaker story, constructed languages / imaginative paracosm influences around the immersive in-world lore of the "16^12" pseudo-historical setting…
Back to the point
The list is far from exhaustive or finished, as life is so much more than meets the eye. But this should be a good start to remind myself what I am working towards, a full revamp of the last ~120 years of history with much attention and care put into making it as satisfying to me as possible, despite the very probable scenario where people take the ideas and incorporate only some of such "modules" in their own workflows. Which is fine but not taking the whole package (and only specific modules) is eventually gonna be a major learning experience for me considering the reason I revamp it all beyond control freak stuff is literally to provide less exclusive / less invasive tools that anyone can learn and customize despite being very... idiosyncratic yk.
Still welcoming suggestions and constructive criticism for such big time, I hope those textual infodumps I do every so often don't bother you too much... Cya soon!
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Like OS/390, z/OS combines a number of formerly separate, related products, some of which are still optional. z/OS has the attributes of modern operating systems but also retains much of the older functionality originated in the 1960s and still in regular use—z/OS is designed for backward compatibility.
Major characteristics
z/OS supports[NB 2] stable mainframe facilities such as CICS, COBOL, IMS, PL/I, IBM Db2, RACF, SNA, IBM MQ, record-oriented data access methods, REXX, CLIST, SMP/E, JCL, TSO/E, and ISPF, among others.
z/OS also ships with a 64-bit Java runtime, C/C++ compiler based on the LLVM open-source Clang infrastructure,[3] and UNIX (Single UNIX Specification) APIs and applications through UNIX System Services – The Open Group certifies z/OS as a compliant UNIX operating system – with UNIX/Linux-style hierarchical HFS[NB 3][NB 4] and zFS file systems. These compatibilities make z/OS capable of running a range of commercial and open source software.[4] z/OS can communicate directly via TCP/IP, including IPv6,[5] and includes standard HTTP servers (one from Lotus, the other Apache-derived) along with other common services such as SSH, FTP, NFS, and CIFS/SMB. z/OS is designed for high quality of service (QoS), even within a single operating system instance, and has built-in Parallel Sysplex clustering capability.
Actually, that is wayyy too exciting for a bedtime story! I remember using the internet on a unix terminal long before the world wide web. They were very excited by email, but it didn't impress me much. Browers changed the world.

23K notes
·
View notes
Text
Benefits We Have Over IBM Post-Warranty Maintenance Services
When your IBM server, storage, or networking equipment reaches the end of warranty, relying on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) support can be costly and restrictive. Our third-party maintenance (TPM) services provide cost-effective, flexible, and efficient alternatives to IBM post-warranty maintenance.
🔹 Why Choose Us Over IBM Post-Warranty Maintenance?
✅ 1. Significant Cost Savings
✔ IBM post-warranty support can be expensive, often requiring businesses to purchase extended OEM contracts. ✔ Our third-party maintenance (TPM) services reduce costs by up to 50-70% while maintaining high service standards.
✅ 2. Flexible & Customizable SLAs (Service Level Agreements)
✔ IBM support often offers one-size-fits-all contracts with limited customization options. ✔ We provide tailored SLAs based on your business needs, including:
24/7/365 support
Next-business-day or 4-hour on-site response times
Remote troubleshooting and proactive monitoring
✅ 3. Extended Hardware Lifespan
✔ IBM may encourage hardware upgrades instead of maintaining EOL (End-of-Life) or EOSL (End-of-Service-Life) equipment. ✔ We specialize in extending the lifecycle of IBM servers, storage, and networking gear, allowing businesses to maximize ROI on existing infrastructure.
✅ 4. Multi-Vendor Support (Beyond IBM)
✔ IBM post-warranty services only cover IBM products, requiring separate contracts for other brands. ✔ Our multi-vendor support model covers IBM and other OEMs like Dell, HP, Cisco, NetApp, Lenovo, etc.
✅ 5. Faster Response & Personalized Support
✔ OEM support queues can be slow, especially for non-critical issues. ✔ Our dedicated engineers and local field support teams ensure faster ticket resolution and direct engineer access—no long hold times!
✅ 6. Spare Parts Availability & Stocking
✔ IBM may limit access to replacement parts for EOL/EOSL hardware, pushing you to upgrade. ✔ We maintain an extensive stock of spare parts to ensure quick replacements and minimize downtime.
✅ 7. Proactive Monitoring & Predictive Maintenance
✔ OEMs typically offer reactive support, addressing issues only after failures occur. ✔ Our TPM services use AI-powered monitoring to predict and prevent failures, reducing unexpected outages.
✅ 8. Seamless Transition & Migration Support
✔ Switching from IBM support can seem complex. ✔ Our seamless onboarding process ensures zero disruption to your business operations during the transition.
✅ 9. Support for Legacy IBM Equipment
✔ IBM often discontinues support for older hardware, forcing unnecessary upgrades. ✔ We provide long-term support for legacy IBM servers, storage, and networking devices, keeping them running efficiently.
✅ 10. Independent & Unbiased Advisory
✔ IBM's goal is to sell new hardware and services, sometimes leading to biased recommendations. ✔ We focus on your actual business needs, offering unbiased guidance on IT maintenance, upgrades, and optimization.
🔹 Our IBM Maintenance Services Cover:
✅ IBM Power Systems (iSeries, AS/400, pSeries, etc.) ✅ IBM System x & BladeCenter Servers ✅ IBM Storage Solutions (Storwize, DS Series, FlashSystem, etc.) ✅ IBM Networking & Mainframes
🚀 Why Settle for Costly IBM Support? Choose a Smarter, More Affordable Alternative!
✔ Save up to 70% on IBM post-warranty maintenance ✔ Get 24/7/365 expert support & flexible SLAs ✔ Extend hardware lifespan & reduce downtime ✔ Access multi-vendor support for all IT infrastructure
💡 Ready to switch? Contact us today for a customized IBM maintenance plan that fits your business needs!

0 notes
Text
iPaaS & Hybrid Future: Easy Integration Allows Innovation

Innovation necessitates an iPaaS approach and a hybrid future.
The next paradigm shift from digital transformation to AI transformation depends on effectively using integration, APIs, events, and data. There are numerous automation and integration methods, but all lead to Integration platform as a service(iPaaS).
In the meanwhile, integrating the required data, applications, and systems is a shifting target. Since apps constantly being updated to the cloud and replaced, the only thing that is constant is change. Furthermore, IDC projects that by 2028, there will be 1 billion new logical applications, partly due to AI. The significant investment in the iPaaS sector is supported by these factors.
This are combining cutting-edge technology from the IBM and webMethods integration portfolios at a time when the market is so innovative and full of opportunities. It goal is to assist company executives in using integration as a competitive advantage via the investments and innovations.
Using experience to create a cohesive hybrid future
It has to be hybrid in order to manage cloud and on-premises installations with ease. Additionally, it has to be unified, combining various integration models with common governance, control, and portability. By combining to knowledge of hybrid and multicloud integration, it is enabling the customers to increase productivity for all individuals and teams involved in integration across their companies. When implemented properly, iPaaS controls complexity to enable businesses to prosper.
With hybrid control at its heart, it use a single control plane to integrate various integration patterns (such files, events, messaging, B2B, apps, APIs, and more) into a shared experience. Your whole integration landscape can be controlled via a single pane of glass, spanning all regions, hybrid multicloud hosting infrastructures, user personas, and teams, with to central management with distributed execution. The most complete platform to manage every use case you can think of is provided by a unified iPaaS.
Using AI-powered solutions to propel iPaaS innovation
Additionally, It have the benefit of being able to provide AI-driven integration solutions that are unrivaled in the iPaaS field because to IBM’s dominant market position in responsible AI, powered by Watsonx. Generative AI may contribute to the whole integration lifecycle, enhancing existing product AI capabilities and promoting productivity and agility in writing, monitoring, and governance for quick innovation. AI assistants are a fantastic place to start, and its’re now using AI agent-led hybrid iPaaS to map a route.
With the realization of this idea, hybrid iPaaS could:
Eliminate integration islands by integrating applications, data, APIs, B2B, files, and event streams into a single platform.
Use a hybrid strategy that connects mainframes and multicloud systems to streamline integration across the company.
Use centralized control and distributed execution runtimes to help guarantee security and data sovereignty.
Throughout the integration lifecycle, generative AI may accelerate typical integration processes, enabling a variety of users to create solutions for their businesses and boosting productivity and agility.
Use events and APIs in conjunction with a modular business architecture to update apps.
By offering a worldwide library that permits reuse and self-service access to current connectors, you may speed up development, save expenses, and enhance data accessibility.
How does iPaaS integration work?
Organizational leaders evaluate integration requirements and objectives prior to selecting and deploying an iPaaS solution. Apps, data storage, microservices, event streams, and other connectors may be made using it platforms. There is seldom an out-of-the-box iPaaS solution that will work for everyone since various iPaaS services are designed to handle different integration requirements and enterprises have varied IT infrastructures.
Teams may choose an iPaaS provider that fits the requirements of the company and start the setup process after identifying integration use cases. Here is an example of how an iPaaS data integration may operate, however initial iPaaS setup procedures will differ depending on it the service a team employs and the kinds of connections they want to make.
Initially, the user must utilize the iPaaS platform’s connectors and templates to link the systems that need integration. For example, a store may decide to integrate a cloud storage service, a customer relationship management (CRM) system, and an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system.
The user may create integration flows, which specify the order of activities (such as taking data from one system, changing it, and moving it to another system), once the systems are linked. The conversion, aggregation, and enrichment procedures that will control the transformation and mapping of data across systems are also specified by users at this point.
The data interchange is then orchestrated by the iPaaS platform, guaranteeing safe, end-to-end data delivery to apps that consume the data or to data lakes and warehouses for further analysis. It will handle authentication, manage API calls, and ensure safe data sharing if the integrations rely on application programming interfaces (APIs).
Teams may monitor dashboards, get alerts, and examine data logs after the linkages are operational to make sure they are operating at their best and that any problems are identified and fixed quickly. Furthermore, a lot of iPaaS solutions are made to expand with the company; as data quantities increase or new systems are introduced, the platform may be set up to roll out more resources.
Companies may also decide to have their own IT teams develop unique integrations. Depending on company requirements, some degree of customization may be required; nevertheless, where feasible, it is often simpler and more economical to rely on third-party iPaaS solutions.
Read more on govindhtech.com
#iPaaSHybridFuture#EasyIntegration#AllowsInnovation#ibm#iPaaS#hybridmulticloud#generativeAI#applicationprogramminginterfaces#API#ai#technology#technews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
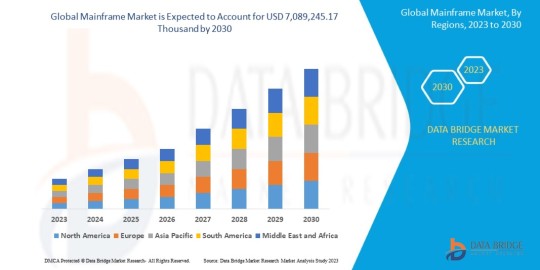
Mainframe Market Size, Share, Trends, Growth and Competitive Analysis
"Global Mainframe Market – Industry Trends and Forecast to 2030
Access Full 350-page PDF Report @
**Segments**
- **Hardware**: The hardware segment of the mainframe market includes the physical components of mainframe systems such as processors, memory, storage devices, and peripherals. These hardware components are essential for the operation of mainframe systems and play a critical role in the performance and reliability of mainframe computers. Companies in this segment focus on designing and manufacturing high-quality, high-performance hardware to meet the demands of enterprise customers.
- **Software**: The software segment of the mainframe market comprises the operating systems, middleware, and applications that run on mainframe systems. Mainframe software plays a vital role in enabling organizations to leverage the power and scalability of mainframe computers for various use cases such as data processing, transaction processing, and analytics. Mainframe software vendors continuously innovate to provide solutions that optimize mainframe performance, security, and manageability.
- **Services**: The services segment of the mainframe market encompasses a wide range of offerings such as maintenance, support, consulting, and training related to mainframe systems. Service providers in this segment help organizations maximize the value of their mainframe investments by ensuring smooth operations, timely upgrades, and efficient utilization of mainframe resources. Mainframe service providers focus on delivering customized solutions to address the specific needs of individual clients.
**Market Players**
- **IBM Corporation**: As a pioneer in mainframe technology, IBM Corporation holds a dominant position in the mainframe market with its zSeries mainframe systems. IBM's mainframe offerings are known for their robustness, reliability, and scalability, making them the preferred choice for many large enterprises worldwide. The company continues to invest in mainframe innovation to meet the evolving needs of modern businesses.
- **BMC Software, Inc.**: BMC Software is a leading provider of mainframe software solutions that help organizations optimize mainframe operations, automate tasks, and improve overall efficiency. The company's mainframe management tools are widely used across industries to streamline processes, enhance security, and reduce costs associated with mainframe operations.
- **The mainframe market is a dynamic and competitive landscape with several key players vying for market share and technological dominance. IBM Corporation stands out as a longstanding leader in mainframe technology, with a rich history of innovation and a comprehensive portfolio of zSeries mainframe systems. IBM's mainframe offerings are renowned for their exceptional robustness, reliability, and scalability, making them a top choice for many enterprise clients worldwide. The company's continuous investment in mainframe innovation underscores its commitment to meeting the evolving needs of businesses in today's digital age.
BMC Software, Inc. is another significant player in the mainframe market, specializing in providing cutting-edge software solutions designed to optimize mainframe operations and enhance overall efficiency. BMC's mainframe management tools are widely adopted across various industries to streamline processes, boost security measures, and drive cost reductions associated with mainframe operations. The company's focus on automation and task optimization resonates well with organizations looking to maximize the value of their mainframe investments while driving operational excellence.
Another notable player in the mainframe market is CA Technologies, a global leader in enterprise software solutions. CA Technologies offers a robust suite of mainframe software products that cater to diverse customer needs, including operating systems, middleware, and applications designed to run seamlessly on mainframe systems. The company's commitment to delivering innovative solutions that enhance mainframe performance, security, and manageability underpins its strong market presence and customer loyalty.
Moreover, Micro Focus International plc occupies a prominent position in the mainframe market, offering a range of software and services tailored to modernizing mainframe environments and optimizing business operations. With a focus on digital transformation and legacy system integration, Micro Focus enables organizations to leverage the power and scalability of mainframe technology while driving innovation and agility in their IT infrastructure.
Overall, the mainframe market is witnessing a shift towards modernization and optimization, driven by the increasing demand for robust and secure computing solutions that can handle vast amounts of data and transaction processing requirements. Market players are continually innovating to**Global Mainframe Market, By Offering (Hardware, Software, and Services), Application (Census Industry, Consumer Statics, ERP and Transaction), Organization Size (Large Enterprises and Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises), End Use (BFSI, IT and Telecom, Government and public sector, Healthcare, Retail, Travel and Transportation, Manufacturing, Others) - Market Trends and Forecast to 2030**.
- The mainframe market is experiencing significant growth and transformation driven by the demand for robust and secure computing solutions that can handle large volumes of data and transaction processing requirements across various industries. The mainframe market is segmented based on offerings into hardware, software, and services, catering to the diverse needs of enterprise customers seeking high-performance computing solutions. The application segments include census industry, consumer statistics, ERP, and transaction processing, reflecting the versatility of mainframe systems in supporting critical business processes.
- In terms of organization size, the mainframe market caters to both large enterprises and small to medium-sized enterprises looking to leverage mainframe technology for their data processing and analytical needs. The end-use segments encompass industries such as BFSI, IT and telecom, government and public sector, healthcare, retail, travel and transportation, manufacturing, and others, highlighting the broad applicability of mainframe systems across different sectors.
- The mainframe market is characterized by intense competition and innovation, with key players like IBM Corporation, BMC Software, Inc., CA Technologies, and Micro Focus International plc leading the market with their cutting
Core Objective of Mainframe Market:
Every firm in the Mainframe Market has objectives but this market research report focus on the crucial objectives, so you can analysis about competition, future market, new products, and informative data that can raise your sales volume exponentially.
Size of the Mainframe Market and growth rate factors.
Important changes in the future Mainframe Market.
Top worldwide competitors of the Market.
Scope and product outlook of Mainframe Market.
Developing regions with potential growth in the future.
Tough Challenges and risk faced in Market.
Global Mainframe top manufacturers profile and sales statistics.
Key takeaways from the Mainframe Market report:
Detailed considerate of Mainframe Market-particular drivers, Trends, constraints, Restraints, Opportunities and major micro markets.
Comprehensive valuation of all prospects and threat in the
In depth study of industry strategies for growth of the Mainframe Market-leading players.
Mainframe Market latest innovations and major procedures.
Favorable dip inside Vigorous high-tech and market latest trends remarkable the Market.
Conclusive study about the growth conspiracy of Mainframe Market for forthcoming years.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Future Market Value for Mainframe Market?
What is the Growth Rate of the Mainframe Market?
What are the Major Companies Operating in the Mainframe Market?
Which Countries Data is covered in the Mainframe Market?
What are the Main Data Pointers Covered in Mainframe Market Report?
Browse Trending Reports:
Smart Agriculture Market Instant Noodles Market Ai In Fashion Market Infantile Hemangioma Market Waste To Diesel Market Contactless Payment Market Necrotizing Enterocolitis Treatment Market Metalized Flexible Packaging Market Customer Analytics Market Plastic Bags Sacks Market Sports Energy Drinks Market Vacuum Packaging Market Pneumococcal Vaccine Market Micro And Nano Plc Market Wireless Medical Device Connectivity Market Herbal Beverages Market Plastic Surgery Devices Market
About Data Bridge Market Research:
Data Bridge set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric Market research and consulting firm with unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market. Data Bridge endeavors to provide appropriate solutions to the complex business challenges and initiates an effortless decision-making process.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC : +653 1251 975
Email: [email protected]"
0 notes
Text
Mainframe access for learning
Mainframe access for learning! get accessible and easily mainframe access at any where any time.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Computer Revolution: Shaping the Modern World
Computers have fundamentally transformed our lives, affecting nearly every aspect of society. From the way we communicate to how we work, learn, and entertain ourselves, the impact of computers is profound and far-reaching. This article explores the history of computers, their evolution, and their role in today’s digital landscape.
The Birth of Computing
The origins of computing date back to the early 19th century with Charles Babbage, often referred to as the "father of the computer." He designed the Analytical Engine, a mechanical device that laid the groundwork for modern computing concepts, including the use of punched cards and memory storage.
However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that computers began to take a more recognizable form. The development of the ENIAC in 1945 marked a significant milestone as it became the first general-purpose electronic computer. With its massive size and limited capabilities, ENIAC demonstrated the potential of electronic computation, paving the way for future innovations.
The Evolution of Computers
Mainframes and Minicomputers: The 1950s and 1960s saw the rise of mainframe computers, which were used primarily by large organizations for complex calculations and data processing. Companies like IBM dominated this market, providing powerful machines that required specialized knowledge to operate. Minicomputers emerged in the 1960s, offering smaller, more affordable options for businesses.
Personal Computers: The 1970s and 1980s marked the arrival of personal computers (PCs), which revolutionized access to computing power. The launch of the Altair 8800 in 1975 is often credited as the catalyst for the home computer revolution. Subsequently, Apple introduced the Apple II, and IBM released the IBM PC, making computers accessible to everyday consumers.
The Internet Age: The advent of the internet in the 1990s transformed computers from standalone machines to gateways for global connectivity. The World Wide Web opened up new avenues for communication, commerce, and information sharing. Computers became essential tools for businesses, educators, and individuals seeking to navigate this vast digital landscape.
Mobile Computing: The 2000s brought about the rise of laptops, smartphones, and tablets, shifting computing from static desktop environments to portable devices. This mobile revolution allowed users to stay connected and productive on the go, further integrating technology into everyday life.
Also Read -
Best PC Computer To Buy – Top Picks For 2025
Current Trends in Computing
Today, computers are more powerful and versatile than ever. Some of the key trends shaping the current landscape include:
Cloud Computing: Cloud technology allows users to store and access data and applications over the internet rather than on local devices. This shift has enabled greater collaboration, flexibility, and scalability for businesses and individuals alike.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI is increasingly integrated into computing, enhancing capabilities in data analysis, natural language processing, and automation. From virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to advanced algorithms powering self-driving cars, AI is redefining what computers can do.
Quantum Computing: Though still in its infancy, quantum computing holds the promise of solving complex problems at speeds unattainable by traditional computers. Researchers are exploring applications in fields such as cryptography, medicine, and materials science.
Cybersecurity: As reliance on computers increases, so do concerns about security. Cyber threats are more sophisticated than ever, prompting organizations to invest heavily in cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and systems.
The Role of Computers in Society
Computers have become essential tools in various sectors, including:
Education: E-learning platforms and educational software have revolutionized teaching and learning. Students can access vast resources, engage in collaborative projects, and connect with educators worldwide.
Healthcare: Computers facilitate advanced diagnostics, telemedicine, and patient record management, improving healthcare delivery and outcomes.
Business: From data analytics to customer relationship management, computers empower businesses to operate more efficiently and make informed decisions.
Entertainment: The gaming and streaming industries have exploded, driven by advancements in computing power. High-performance computers enable immersive gaming experiences and seamless content streaming. The Future of Computing
As we look ahead, the future of computing promises even more transformative developments. Emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are set to enhance user experiences in gaming, training, and remote collaboration. Furthermore, the continued evolution of AI will likely lead to even more intelligent systems that can learn and adapt.
Sustainability will also play a crucial role in the future of computing, with an increasing focus on energy-efficient hardware and responsible recycling practices.
Conclusion
The computer revolution has reshaped our world in unimaginable ways. From their humble beginnings to the powerful machines we use today, computers have become central to our lives, influencing how we work, learn, and interact. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for innovation is limitless, ensuring that computers will remain at the forefront of societal change for years to come.
Explore more - JayXop
1 note
·
View note
Text
Story of SaaS?

"SaaS" is a term that’s hard to ignore but what exactly does it mean? Imagine instead of dealing with the hassle of downloading and installing software on every device, you can access what you need instantly through the internet. That’s SaaS, or Software as a Service, a cloud-based solution that makes software more accessible, flexible, and user-friendly. Want to understand why SaaS is reshaping the way we use technology so let’s dive in!
Definition of SaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a software distribution model in which applications are hosted by a service provider or vendor and made available to customers over the internet. This model contrasts with traditional software, where the software is purchased and installed on local machines or servers.
The concept of SaaS dates back to the 1960s when IBM and other companies offered mainframe computers on a time-sharing basis. However, the modern SaaS model we are familiar with started to gain traction in the late 1990s and early 2000s with the advent of the internet and advancements in cloud computing technology. Companies like Salesforce were pioneers in this space, demonstrating the potential of delivering software via the web. Proket is also a good example of Saas based CRM software where realtors get the feature of landing page builder for their PPC ad campaigns within seconds.
SaaS vs. Traditional Software
Traditional software models often require substantial upfront costs, installation on local machines, and ongoing maintenance. SaaS, on the other hand, is subscription-based, does not require installation, and is maintained by the service provider. This shift from ownership to service has made SaaS a popular choice among businesses of all sizes.
Key Characteristics of SaaS
Accessibility and Flexibility
One of the standout features of SaaS is its accessibility. Users can access the software from any device, at any time, as long as they have an internet connection. This flexibility allows teams to collaborate more effectively, regardless of location.
Cost-Effectiveness
SaaS typically operates on a subscription-based pricing model, which can significantly reduce the upfront costs associated with purchasing traditional software. This model also allows businesses to scale their usage based on their needs, paying only for what they use.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance
With SaaS based CRM updates and maintenance are handled by the service provider. This means users always have access to the latest features and security updates without having to manage these tasks themselves. It’s a hassle-free experience that ensures your software is always up-to-date.
Scalability and Integration
SaaS solutions are designed to scale easily with your business. Whether you need to add more users or integrate with other software solutions, SaaS platforms can adapt to your growing needs. This scalability is crucial for businesses that are expanding or experiencing fluctuating demand.
How SaaS Works
The Cloud Computing Foundation
SaaS is built on the foundation of cloud computing. This means the software is hosted on the cloud, and users access it via the internet. The cloud infrastructure is managed by the SaaS provider, which includes servers, databases, and networking components.
Cloud Infrastructure
The cloud infrastructure supporting SaaS is robust and designed to handle multiple users simultaneously. This infrastructure is typically spread across multiple data centers to ensure high availability and redundancy. The use of cloud technology allows SaaS providers to offer reliable and scalable services to their users.
SaaS Deployment Models
There are different deployment models for SaaS, including public, private, and hybrid clouds. Public SaaS is available over the internet and is accessible to any user with the necessary credentials. Private SaaS is hosted on a private cloud and is often used by organizations with specific security or compliance needs. Hybrid SaaS combines elements of both public and private deployments.
Subscription-Based Pricing Model
One of the defining features of SaaS is its subscription-based pricing model. Instead of purchasing a software license, users pay a recurring fee to access the software.
Benefits of Subscription Model
The subscription model offers several benefits, including predictable costs, flexibility to scale usage, and access to regular updates. It also reduces the financial burden of large upfront software purchases, making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
Common SaaS Pricing Tiers
SaaS providers typically offer several pricing tiers to cater to different user needs. These tiers might include basic, standard, and premium plans, each offering varying levels of features and support. This tiered approach allows users to choose the plan that best fits their requirements and budget.
Advantages of SaaS
Enhanced Collaboration
SaaS tools are designed with collaboration in mind. They allow multiple users to access the same platform, share documents, and work together in real-time. This level of collaboration is particularly beneficial for remote teams and global organizations.
Reduced Time to Deployment
SaaS applications can be up and running in a matter of hours or days, compared to traditional software, which might take weeks or even months to deploy. This rapid deployment means businesses can start using the software almost immediately, without lengthy installation processes.
Global Accessibility
Because SaaS is delivered via the cloud, it’s accessible from anywhere in the world. This global accessibility is a significant advantage for businesses with distributed teams or international operations, allowing them to maintain consistent workflows regardless of geographic location.
Automatic Software Updates
With SaaS, users don’t need to worry about manually updating their software. The service provider takes care of all updates, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and security patches. This automatic update process helps maintain software efficiency and security.
Popular Examples of SaaS
Proket
Proket, a leading SaaS customer relationship management (CRM) platform which offers various features like landing page creation for lead generation, project management, lead nurturing, team management and much more.
Google Workspace
Google Workspace, formerly known as G Suite, is a suite of productivity and collaboration tools, including Gmail, Google Docs, and Google Drive. It’s a prime example of how SaaS can enhance collaboration and efficiency within teams.
Microsoft 365
Microsoft 365 offers a suite of tools similar to Google Workspace, including Word, Excel, and Outlook. It’s available as a SaaS product, allowing users to access Microsoft’s powerful productivity tools from anywhere.
Zoom
Zoom has become synonymous with video conferencing, especially in the post-pandemic era. As a SaaS platform, Zoom allows users to host and join virtual meetings, webinars, and conferences with ease.
Final Words
SaaS has transformed the way we interact with software, offering unmatched convenience, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. By eliminating the need for complex installations and ongoing maintenance, SaaS enables businesses and individuals to access cutting-edge technology from anywhere, at any time. Whether it's for collaboration, productivity, or specialized tools like Proket’s CRM, SaaS solutions are designed to meet the evolving demands of the digital age. As more organizations embrace cloud-based services, the impact of SaaS on the global technology landscape will only continue to grow.
#lead generation for realtors#Best Landing Page Software with CRM#CRM Landing Page Builder#Best Landing Page Software 2024#Landing Page Builder with CRM
0 notes
Text
Understanding the fundamentals of business automation

Automation has impacted practically every industry throughout the years, including healthcare systems, assembly lines, and ATMs. However, automation is being elevated to a whole new level by machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI). The way people and machines interact is changing as a result of this so-called "intelligent automation," which enables organizations to grow their clientele, boost productivity, and succeed in competitive marketplaces. In actuality, studies demonstrate the enormous financial advantages of automation. According to the IBM Institute for Business Value, AI-enabled automation will produce a labor value of billions of dollars in 2022 alone. This essay examines how business automation is evolving, why it's important now, and what to think about if you want to use automation in your own company.
Business automation: What is it?The use of technology to automate monotonous operations and free up employees for higher-value work is known as business automation. This covers robotic process automation (RPA), business process automation (BPA), and automation driven by artificial intelligence. Automation used to require enormous mainframes and a team of specialists to maintain them. These days, businesses of all sizes may access the capabilities thanks to cloud-based automation tools.
The following are some examples of business automation types:
1. Basic automation: Basic automation is the process of automating basic, elementary tasks. Basic automation technologies digitize repetitive activities with little to no coding, reducing errors and speeding up transactional activity. Two instances of basic automation are RPA and business process management (BPM). 2. Process automation: Process automation maintains consistency and openness in company processes. Process automation, which is frequently managed by specialized software, can boost output and efficiency while also providing insightful business data. Examples of process automation include workflow automation and process mining.
3. Advanced automation: This type of automation integrates many systems inside an organization by combining human and machine capabilities. Advanced automation, which facilitates intricate procedures, depends on unstructured data in conjunction with machine learning, natural language processing, and analysis. It encourages decision support for specialized work and knowledge management.
4. Intelligent automation: AI-powered intelligent automation enables robots to "learn" and decide for themselves depending on scenarios they have seen and examined. AI-powered virtual assistants, for instance, can lower expenses in customer service while facilitating more intelligent interactions between customers and human workers. An improved level of customer service is the outcome.
What makes business automation crucial?
Automation is a wonderful approach to accelerate business growth and streamline processes, regardless of the size of your company. Automation tools allow you to shift human labor to other areas of the business by substituting machine labor for human labor.
Businesses must continuously use best practices and tested automation software across all workflows to fully benefit from automation. This includes streamlining internal procedures and enabling faster-digitized consumer experiences.
Nevertheless, not every solution has every piece of technology required to automate end-to-end processes. This may result in several-point solutions, increased expenses, and a scalability issue.
Business automation advantages: Business automation is essential in a world that is changing quickly. It can be difficult to foresee which customer behaviors, such as sharply changing demand or increased health and safety concerns, would endure beyond the pandemic.
However, you do have some control over how you handle the experiences you give your clients. You can improve or adjust these experiences with automation, particularly when it's paired with AI. This will increase revenue, make better use of your resources, and boost customer pleasure. Using an automation platform that assists you in doing the following is one of the greatest ways to accomplish this:
1. Identify procedures: Identify areas of your business where there are inefficiencies or hotspots to assist decide where automated procedures can have the biggest impact. Modeling and process mining are involved in this.
2. Apply intelligence: Make recommendations for actions based on data from automating your processes using AI and machine learning, freeing up personnel for more strategic duties.
3. Expand your personnel: Create RPA tools and send out digital workers to work alongside people whenever increased productivity may be attained or when support is required.
4. Automate core operations: To satisfy business demands, apply fundamental automation capabilities—document processing, workflow orchestration, content services, and decision management—to critical operational areas.
#Business Automation Experts#Business Automation Consultants#Business Process Consultant#Business Management Solutions
0 notes
Text
What is z/OS in Mainframe?
Originally designed for large-scale computations, Mainframes now meet modern enterprise demands. From early models to today’s sophisticated systems, mainframes showcase continuous innovation.
At the heart of modern mainframe computing is z/OS, IBM’s premier operating system for Z series mainframes. z/OS provides a reliable, secure, and scalable platform for mission-critical applications, supporting diverse workloads from batch processing to online transaction processing (OLTP).
Core Features of z/OS
High Availability and Scalability : z/OS is renowned for its high availability, designed to minimize downtime and ensure continuous operation during hardware failures or system upgrades. Its scalability allows organizations to handle increasing workloads without compromising performance.
Advanced Security Mechanisms : Security is paramount in today’s digital landscape, and z/OS excels here. It offers advanced encryption, multi-level security policies, and rigorous access controls, making it a preferred choice for industries like finance, healthcare, and government where data integrity and confidentiality are essential.
Workload Management : Efficient workload management is vital for optimal system performance. z/OS’s Workload Manager (WLM) dynamically allocates resources based on workload priorities, ensuring responsive and efficient operations across all applications.
Technical Architecture of z/OS
System Components and Structure: The architecture of z/OS includes numerous components working in harmony for exceptional performance. Key components like the Job Entry Subsystem (JES), Resource Management Facility (RMF), and System Management Facility (SMF) are crucial to its functionality.
Virtualization and Resource Management: Virtualization is central to z/OS, allowing multiple logical partitions (LPARs) to run on a single physical mainframe. The z/OS hypervisor, PR/SM (Processor Resource/System Manager), ensures efficient resource utilization and workload isolation.
Subsystems and Middleware Integration: z/OS supports subsystems and middleware, including CICS (Customer Information Control System), IMS (Information Management System), and DB2. These tools are essential for transaction processing, database management, and application integration, enhancing the platform’s versatility.
The Future of z/OS
Innovations and Technological Advancements : The future of z/OS is promising, with continuous innovations. IBM is enhancing z/OS with machine learning, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytics, elevating its capabilities to meet modern enterprise demands.
Integration with Modern Technologies : z/OS integrates with contemporary technologies such as cloud computing, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These integrations transform z/OS into a versatile platform, supporting a wide array of modern applications and services.
Combining decades of innovation with cutting-edge features, z/OS delivers a powerful and versatile platform. Its role in supporting mission-critical applications across various industries underscores its importance, reaffirming its position as a leader in enterprise computing.
0 notes
Text
Unlocking the Power of IBM CICS: Online Training Programs that Deliver Results
IBM CICS (Customer Information Control System) is a powerful mainframe transaction processing system that has been an integral part of the business world for over 50 years. With its ability to handle high volumes of transactions, CICS has been a key player in driving the success of various industries, including banking, insurance, and retail. However, as technology continues to evolve rapidly, professionals must keep up with the latest advancements in CICS in order to harness its potential fully. This is where online training programs come into play. With the convenience of online learning, professionals can enhance their skills and knowledge of IBM CICS, unlocking its full potential and staying ahead in the competitive market. In this article, we will explore the power of IBM CICS and how online training programs can provide the necessary resources and support for professionals to achieve their goals. From the basics of CICS to advanced features and techniques, these training programs are designed to deliver results and equip professionals with the necessary tools to succeed in their respective fields. Let's delve into the world of IBM CICS and discover how online training programs can unlock its true power.
Expert-led courses for IBM CICS
Our online training programs for IBM CICS offer a comprehensive and in-depth approach to mastering this powerful mainframe transaction processing system. Developed and led by industry experts with extensive experience in CICS, these courses provide valuable insights and practical knowledge that can be immediately applied in real-world scenarios. Through a combination of informative lectures, hands-on exercises, and interactive discussions, participants gain a deep understanding of CICS architecture, administration, programming, and performance optimization. Our expert instructors guide learners through complex concepts and best practices, ensuring that they acquire the skills necessary to manage and enhance CICS environments efficiently. With our expert-led courses, individuals and organizations can unlock the full potential of IBM CICS and stay ahead in today's rapidly evolving technology landscape.
Flexible training options for professionals
To cater to professionals' busy schedules and diverse learning preferences, we offer a range of flexible training options for our IBM CICS online programs. We understand that professionals may have limited time to dedicate to training, which is why our courses are designed to be accessible at any time and from anywhere. With the convenience of self-paced learning, participants can progress through the program at their own speed, fitting it seamlessly into their work and personal commitments. Additionally, we provide the option for live virtual classrooms, where participants can engage in real-time discussions with instructors and fellow professionals, promoting interactive learning and collaboration. This flexibility ensures that professionals can choose the training format that best suits their needs and maximizes their learning experience. Whether they prefer the convenience of self-paced learning or the dynamic environment of live virtual classrooms, our flexible training options empower professionals to enhance their skills and achieve their career goals efficiently and effectively.
Hands-on learning with real-world applications
Our online training programs are designed to provide participants with hands-on learning experiences that have real-world applications. We believe that true mastery of IBM CICS can only be achieved through the practical application of the concepts learned. That is why our courses incorporate interactive exercises and simulations that allow participants to apply their knowledge in simulated real-world scenarios. Through these activities, participants gain valuable experience in problem-solving, troubleshooting, and decision-making, which are essential skills in a professional setting. By engaging in hands-on learning with real-world applications, participants can develop a deeper understanding of IBM CICS and confidently apply their skills to address complex challenges in their work environments.
Enhance your CICS skills today.
In an ever-evolving digital landscape, professionals in the IT industry must enhance their skills to stay competitive continuously. The power of IBM CICS is unparalleled, and those who possess a strong command of this technology can unlock a multitude of opportunities. Whether you are a seasoned professional or just starting your career in mainframe systems, our online training programs offer comprehensive and immersive learning experiences that will take your CICS skills to new heights. Our expert instructors, who have extensive industry experience, will guide you through a carefully crafted curriculum that covers the essential aspects of IBM CICS. From mastering the fundamentals to exploring advanced functionalities, our courses are designed to equip you with the knowledge and practical skills needed to excel in your role. Don't miss out on the chance to enhance your CICS skills and pave the way for a successful and rewarding career in the world of mainframe systems. Invest in your professional development today and unlock the power of IBM CICS with our online training programs.
Achieve success with online training.
In today's digital age, online training has emerged as a powerful tool for professional development, allowing individuals to achieve success in their chosen fields. By opting for online training programs, professionals can benefit from the convenience of flexible learning schedules and the ability to access course materials from anywhere in the world. Our carefully curated online training programs for IBM CICS offer a unique opportunity to unlock the power of this technology and gain a competitive edge. With a robust curriculum and expert instructors, these programs provide comprehensive coverage of essential concepts and advanced functionalities, ensuring that participants develop a strong command of IBM CICS. Whether you are seeking to upskill or enhance your existing knowledge, our online training programs deliver results by equipping you with the skills and expertise needed to excel in the rapidly evolving IT industry.
In conclusion, IBM CICS is a powerful tool that has been a staple in many enterprises for decades. With the availability of online training programs, individuals and organizations can now unlock the full potential of this software and stay on top of the constantly evolving technology landscape. By investing in these training programs, one can expect to see significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and overall success. As IBM CICS continues to evolve, it is crucial to stay updated and knowledgeable, and these training programs offer the perfect opportunity to do so. So, don't wait any longer and start unlocking the power of IBM CICS today.
0 notes